|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
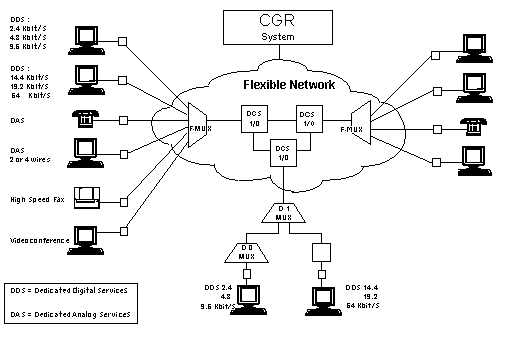
CGRManagement System for Flexible Data Transmission NetworksIntroductionThe need to offer ever more reliable and customizable data transmissionservices to meet the needs of many different kinds of clients has brought abouta data transmission network known as Flexible Network. The network hastransmissive infrastructures allowing high flexibility in digital connections.lt is also equipped with management tools able to provide constant monitoring ofthe status of employed resources and of the configuration of transmissivesupports, guaranteeing high standards of quality and the ability to offer aseries of services, such as: -Point-to-point digital connectivity-Multi-point digital connectivity-Time management of the connections-Bandwidth optimization-Realization of Virtual Private Networks (VPN).The typical fields of application for the services offered by the FlexibleNetwork are data transmission between computers, PCs and terminals (remoteprocessing, transferring directory contents between computers, banktransactions, reservations); interconnecting Local Area Networks (LANs);interconnecting exchanges (PABX); transmitting newspapers to remote locations. The Flexible Network also allows to realize the connections to provideaccess to the Packet Network (digital connections up to 64 kbit/s), to the VoiceNetwork, to the Videoconferencing Service, as well as the connections for theTimed Direct Digital Circuits (CDN-T) Service.
Fig.1 - Architecture of the Flexible Network The SystemCGR is the Centralized Management System for the Flexible Network, developedby TELESOFT S.p.A. for TELECOM ITALIA. It allows remote controlover all the functionalities of the Digital Cross Connects (DCS 1/0) and of theFlexible Multiplexers (F-MUX) and it also contains the updated record of everyresource present on the Flexible Network, enabling the implementation of operationand maintenance procedures for managing available services more efficiently and for providing new services. In particular, CGR offers the following benefits: · Lower connection activation times
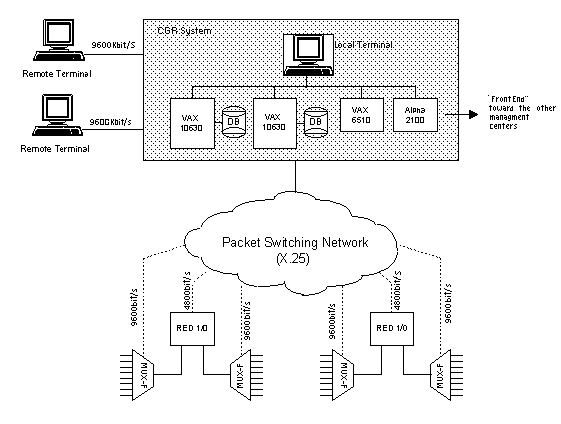
· Ability to re-route a failed connection on a pre-definedback-up · "Timed Digital Direct Circuits" and "DedicatedVirtual Private Networks" services. System ArchitectureThe CGR system's hardware architecture is based on a central host connectedto the flexible network's devices. Within TELECOM ITALIA's network, theconfiguration comprises two mainframes (DECVAX 10630) and computers (DECVAX6510) connected by means of X.25 links to the network's DCS and F-Mux. The system's terminals are both positioned locally, for system management,and in remote sites for the flexible network's operators.
Fig.2: Telecom Italia System Architecture There is also a fourth computer, an Alpha 2100 (DEC Osf-1), connected in thenetwork and acting as a "Front End" towards the other managementcenters (Fig. 2). The particular hardware and software configuration (Cluster) allows theManagement Center's computers to operate sharing the load. Should one of themain computers fail, the remaining operational computer is able to perform allactivities required for the proper operation of the center. The CGR's database is contained in a mass storage drive comprising varioustypes of disks for a total of about 10 Gbytes. All network information isstored only on half of these disks, since the other half is used as a hotback-up to safeguard the data (shadowing). Given the CGR's importance for the operation and maintenance of the FlexibleNetwork in addition to the full duplication of the center's essentialcomponents, a second center - identical to the first but in another location -is also provided, and activated automatically in case of need. FunctionsThe following is a summary of the main functions perfomed by the "CGRManagement Center": Networks Devices and Configuration ManagementIn the case of the 1/0 DCSs and of the flexible Multiplexers, with which theCGR can dialog through a monitoring channel, direct management is enforced,allowing:
For all other devices, the CGR performs indirect management by storing thefollowing information in its DB:
Networks Resources Managementthis allows to partition the network according to "physical pool"and "logic pool" criteria, to ensure an adequate partition and use ofthe network's resources among the different services:
Permanent Circuits Managementthis allows the remote activation of permanent circuits for datatransmission, and it also provides support in the circuit design activity, bothfor main and back-up circuits. Timed Circuits ManagementThe CGR allows to reserve the automatic (timed) activation of thecross-connects for Flexible Network connections. Activation of a Timed Circuitcan be reserved in advance in one of the following ways:
Virtual Private Networks ManagementThe CGR allows to permanently assign a subset of Flexible Network resourcesto a user to constitute an actual sub-network (Virtual Private Network logicpool). Within this sub-network, the client can set up, disconnect and route hisown circuits through a video terminal connected to the CGR. Remotely Circuits Diagnosisit allows, using equipment deployed on the network, to effect remoteecircuits diagnosis up to the client's home. Alarms Managementit provides real-time monitoring of the network's operating condition bycollecting alarms detected by the Digital Cross Connects (DCC)and by theFlexible Multiplexers and indicates them to the operators. Moreover, when an alarm indication arrives from a network device, the CGRdetermines which circuits are involved in the alarm, and for each circuit itgenerates the alarmed circuit event, presenting it to the operator. Quality Data Managementthis monitors the availability and transmission quality of each 2 Mbit/sstream of the network joining the DCCs to each other and the DCCs to the F-MUX,and it uses these data to compute the availability and quality data for each user circuit. System Managementit provides the functionalities required to ensure alignment between thelocal databases of directly managed network devices (F-MUX and DCC) and theCGR's own centralizad database. Managed DeviceThe system manages Digital Cross Connects 1/0, Flexible Multiplexers, 2Mbit/s multiplexers (MUX-D, MUX-PCM, etc.), 64 kbit/s sub-multiplexers (SMUX-BC,SWX-H, etc.), user connection terminals (MBB-AV, MBB+, etc.), network terminals(DCEL, DCE2, DCE+, DCE3). Hardware and Software RequirementsThe system architecture requires for hardware and software porting ontoother technological platforms; hardware size can be scaled according to the loadinduced by the controlled network. Software de Base
Hardware de Base
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
E-mail: company@tlsoft.ru Contact information |
Copyright © 1996-1998 Telesoft Russia |